Bridging Eastern & Western Medicine
Discover How to Alleviate Your Migraine & Headache with MBR Therapy
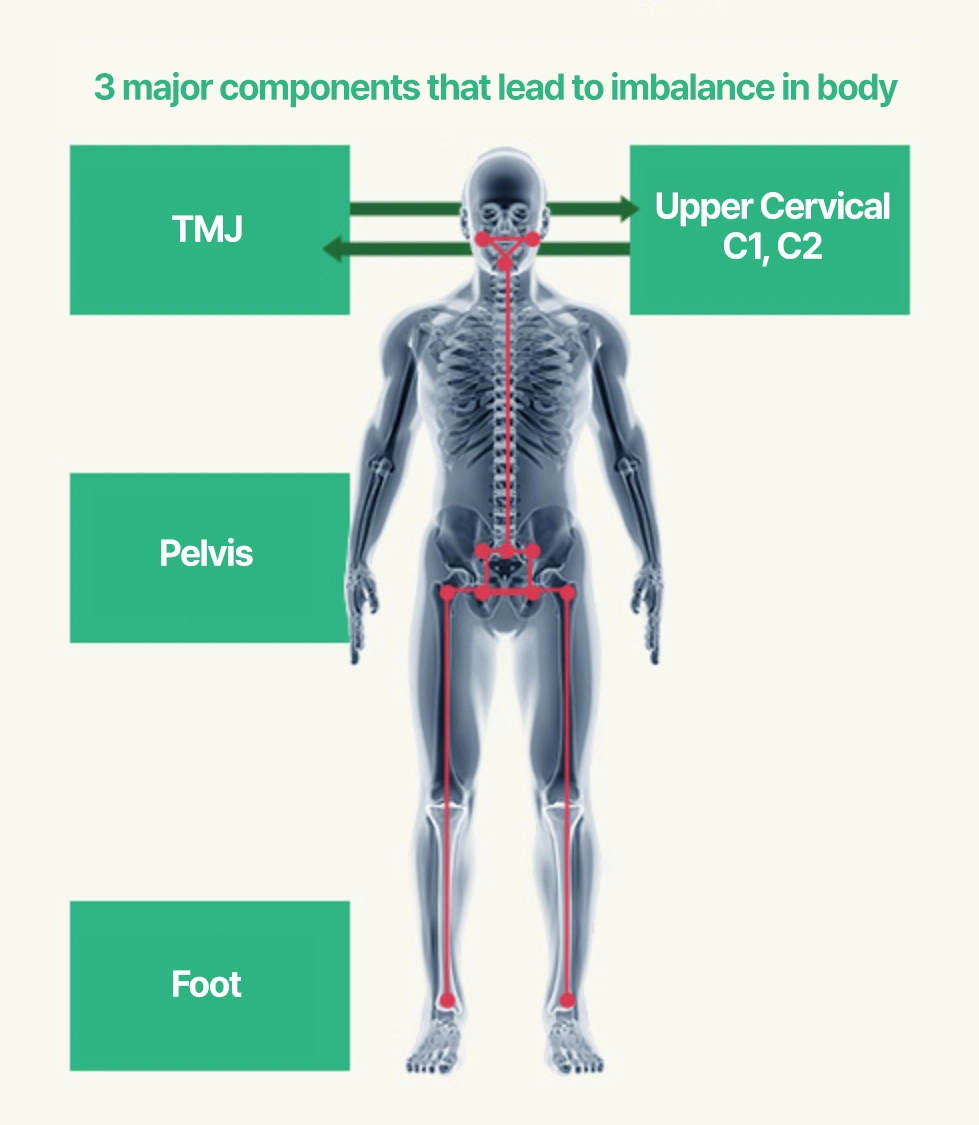

Major contributor to migraine, neck, and shoulder pain
Is the Brain the Cause of Migraines & Headaches?
When experiencing a headache or migraine, individuals often assume that the brain is the underlying cause. However, if CT scans and MRI scans reveal no abnormalities, it is probable that the source of the problem lies elsewhere. What other factors could potentially be responsible?
Interestingly, brain tissue and brain cells do not possess pain receptors. The transmission of pain signals likely originates from the pain-sensitive complex, where numerous nerve endings are concentrated. Even the slightest stimulation of this complex can trigger pain. Migraines and headaches occur when the pain-sensitive complex becomes strained, compressed, inflamed, or irritated.
The Most Effective Way to Adjust the Delicate Pain-sensitive Complex is Using MBR Therapy
Major contributor to migraine, neck, and shoulder pain
Root Causes of
Headache & Migraine
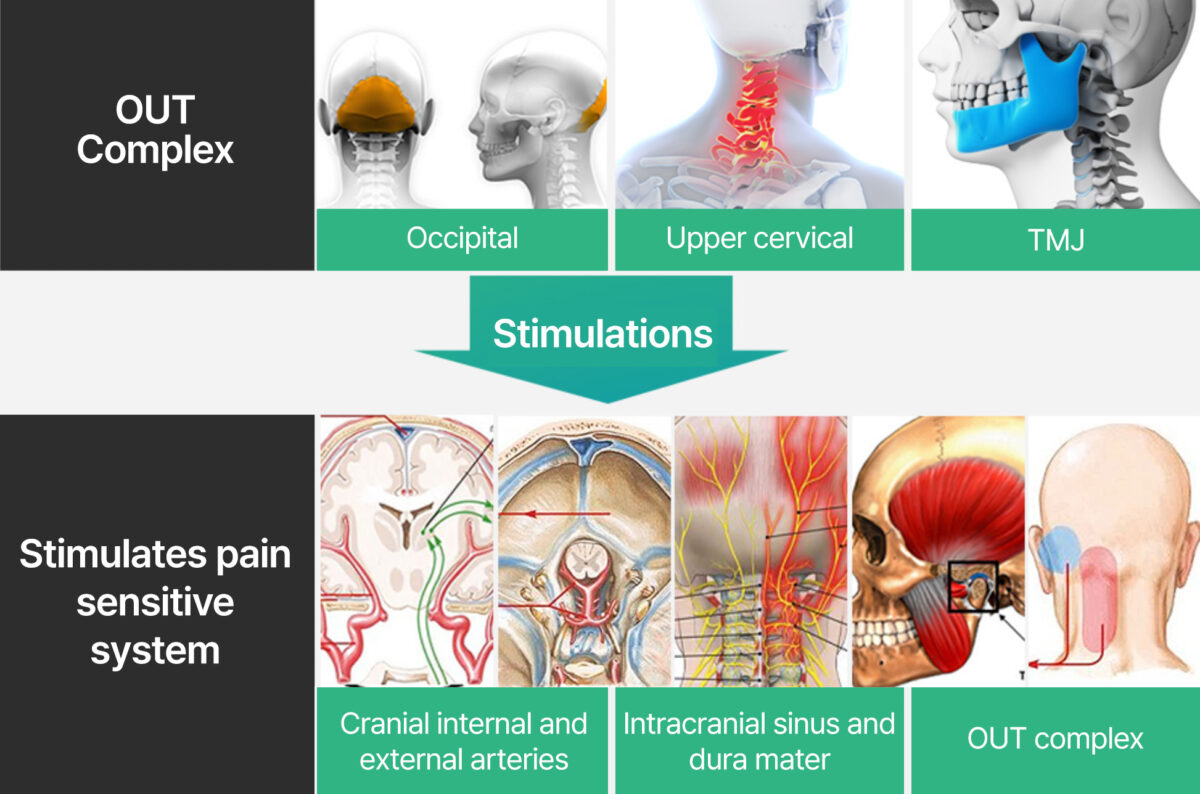
Chronic headaches are categorized into six patterns based on the misalignment of the OUT-Complex, which includes brain arteries, veins, and venous sinuses, dura, vascular vessels at the base of the skull, cranial nerves 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10, as well as muscles, myofascial tissues, and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connecting the nerves in the occipital head, head, neck, and shoulders. The pain-sensitive structures mentioned are vulnerable to pulling, twisting, and pressure, leading to headache symptoms.
The misalignment of the OUT-Complex acts as a trigger, stimulating the pain-sensitive structures. This misalignment serves as the root cause of headaches, ultimately resulting in the activation of the pain-sensitive system.
Step-by-Step
Type of Chronic Headache
Type 1. Migraines can only be alleviated by undisturbed sleep
These migraines are triggered by the stimulation of the cervical nerve, which occurs due to degenerative changes in the occipital joint.
Type 2. Pain around eyebrows
Type 3. Severe Neuralgia
Type 4. Trigeminal neuralgia, affecting half of the head and face
This type of migraine is caused by the stimulation of the trigeminal nerve. This stimulation can be attributed to issues such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems and deviation of the C1 and C2 vertebrae.
Type 5. TMJ headache due to imbalance of the jaw joints
Type 6. Muscle tension headache
Type 7. Post-traumatic headache after concussion
Type 8. Headache due to indigestion
Headaches resulting from indigestion are caused by the stimulation of the cranial nerve due to the digestive issues.
The Korean Medical Classification
Types of Headaches According to Differential Diagnosis
Stress Type
(Liver Qi Stagnation)
(Phlegm Obstruct the Channel)
Respiratory type
(Oxygen supply)
